Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Journal papers
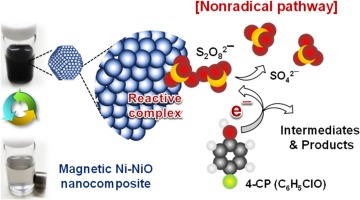
The nanocomposite of metallic nickel and nickel oxide (denoted as Ni–NiO), synthesized by a simple sol–gel method, was found to activate peroxydisulfate (PDS), resulting in the effective oxidation of phenolic compounds and selected pharmaceuticals. A nonradical mechanism was proposed to explain the activation of PDS by Ni–NiO, in which organic contaminants are believed to be oxidized through an electron abstraction pathway mediated by the reactive complexes formed between PDS and the Ni–NiO surface. This mechanism was supported by multiple lines of evidence including radical scavenger experiments, the oxidation products, linear sweep voltammetry, and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. The Ni–NiO/PDS system exhibited a PDS utilization efficiency (expressed by the ratio of degraded organic contaminant to decomposed PDS) that was over 80%, and Ni–NiO showed a greater activity for PDS activation than a commercial nanoparticulate nickel oxide. This improved performance of Ni‒NiO was attributed to the disproportioned incorporation of the metallic Ni into the NiO matrix, creating more sites with oxygen vacancy. Also owing to the metallic Ni, Ni–NiO possessed magnetic properties and therefore could be easily separated and reused.