Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Journal papers
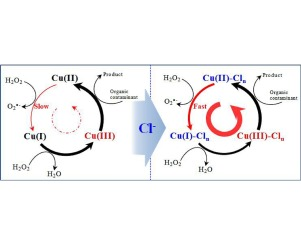
The Cu(II)-catalyzed Fenton-like reaction was found to be significantly accelerated in the presence of chloride ion (i.e., the Cu(II)/H2O2/Cl− system), enhancing the oxidative degradation of organic contaminants at neutral pH. The degradation of carbamazepine (a select target contaminant) by the Cu(II)/H2O2 system using 1 μM Cu(II) and 10 mM H2O2 was accelerated by 28-fold in the presence of 10,000 mg/L Cl− at pH 7. The observed rate of carbamazepine degradation generally increased with increasing doses of Cu(II), H2O2, and Cl−, and exhibited an optimal value at around pH 7.5. Various other organic contaminants such as propranolol, phenol, acetaminophen, 4-chlorophenol, benzoic acid, and caffeine were also effectively degraded by the Cu(II)/H2O2/Cl− system. Experiments using oxidant probe compounds and electron paramagnetic spectroscopy suggested that cupryl (Cu(III)) species are the major reactive oxidants responsible for the degradation of these organic contaminants. The enhanced kinetics was further confirmed in natural seawater.