Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Journal papers
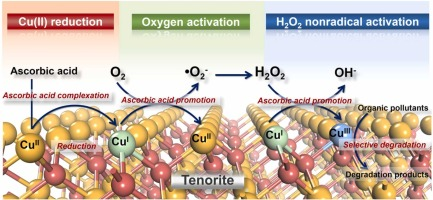
This study constructs a novel strategy for the activation of molecular oxygen over naturally abundant tenorite (CuO) complexed with ascorbic acid (AA). According to the results of ATR-FTIR characterization and DFT calculation, AA forms inner-sphere complexes with copper on the CuO surface ( Cu(II)) in a monodentate mononuclear configuration, reduces
Cu(II)) in a monodentate mononuclear configuration, reduces  Cu(II) to
Cu(II) to  Cu(I), and complexes the latter species to efficiently activate molecular oxygen for the in situ production of H2O2 and subsequently generate reactive oxidants for the degradation of organic compounds. The multiple evidence of oxidant scavenging tests, EPR spectroscopy, molecular probe experiments, and XPS and XANES analyses collectively suggest that the dominant reactive oxidant is the surface-bound high-valent copper species (
Cu(I), and complexes the latter species to efficiently activate molecular oxygen for the in situ production of H2O2 and subsequently generate reactive oxidants for the degradation of organic compounds. The multiple evidence of oxidant scavenging tests, EPR spectroscopy, molecular probe experiments, and XPS and XANES analyses collectively suggest that the dominant reactive oxidant is the surface-bound high-valent copper species ( Cu(III)) rather than •OH. Compared with •OH,
Cu(III)) rather than •OH. Compared with •OH,  Cu(III) possesses the different oxidation behaviors for bisphenol A and benzoic acid and is less reactive toward alcohols and compounds with strongly electron-withdrawing groups and heterocyclic rings. The CuO/AA system exhibits stable performance that is only marginally affected by the water matrix and shows high durability in repetition tests. Thus, this work describes a promising strategy for the oxidation of organic contaminants via the activation of molecular oxygen and provides insights into the properties and identifications of the
Cu(III) possesses the different oxidation behaviors for bisphenol A and benzoic acid and is less reactive toward alcohols and compounds with strongly electron-withdrawing groups and heterocyclic rings. The CuO/AA system exhibits stable performance that is only marginally affected by the water matrix and shows high durability in repetition tests. Thus, this work describes a promising strategy for the oxidation of organic contaminants via the activation of molecular oxygen and provides insights into the properties and identifications of the  Cu(III) species.
Cu(III) species.