Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Journal papers
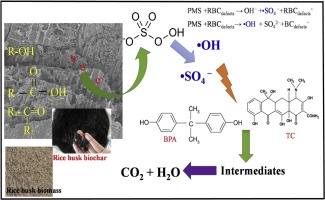
In this study, novel activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by biochar derived from rice husk (generally considered useless agricultural wastes in Vietnam) toward organic pollutants from wastewater was investigated. The basic properties of biochar were characterized through field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), elemental analysis (EA) and gas adsorption analysis (BET). Operating parameters including PMS concentration, dose of biochar and initial concentration of target pollutants (tetracycline and bisphenol A) were systematically studied. The results showed that biochar derived from rice husk effectively activated of PMS, leading to high degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. The degradation efficiency of organic pollutants increased with increasing PMS concentration and amount of biochar. The reuse of rice husk biochar and the possible mechanism for PMS activation were proposed accordingly. In addition, the evaluation of potential available rice husk biomass in Vietnam was discussed. These findings suggest a novel rice husk biochar for activation of PMS toward toxic organic pollutants from wastewater.