Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Publication
Advanced Redox Technology Lab
Journal papers
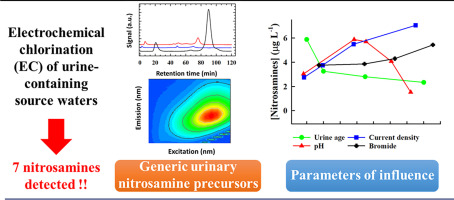
We investigated the formation of nitrosamines from urine during electrochemical chlorination (EC) using dimensionally stable anodes. Short-term electrolysis (< 1 h) of urine at 25 mA cm−2 generated seven nitrosamines (0.1–7.4 µg L−1), where N-nitrosodimethylamine, N-nitrosomethylethylamine, and N-nitrosodiethylamine were predominant with concentrations ranging from 1.2 to 7.4 µg L−1. Mechanistic studies showed that the formation kinetics of nitrosamines was influenced by urine aging and composition, with fresh urine generating the highest levels (0.9–5.8 µg L−1) compared with aged, centrifuged, or filtered urine (0.2–4.1 µg L−1). Concurrently, studies on urine pretreatment through filtration and centrifugation underscored the significance of nitrogenous metabolites (such as protein-like products and urinary amino acids) and particle-associated humic fractions in nitrosamine formation during EC of urine. This finding was confirmed through chromatographic and spectroscopic studies utilizing LC OCD, Raman spectra, and 3DEEM fluorescence spectra. Parametric studies demonstrated that the ultimate [nitrosamines] increased at a pH range of 4.5–6.2, and with increasing [bromide], [ammonium], and current density. Conversely, sulfate and carbonate ions inhibited nitrosamine formation. Moreover, the implications of EC in urine-containing source waters were evaluated. The results indicate that regardless of the urine source (individual volunteers, septic tank, swimming pool, untreated municipal wastewater), high levels of nitrosamines (0.1–17.6 µg L−1) were generated, surpassing the potable reuse guideline of 10 ng L−1. Overall, this study provides insights to elucidate the mechanisms underlying nitrosamine formation and optimize the operating conditions. Such insights facilitate suppressing the generation of nitrosamine byproducts during electrochemical treatment of urine-containing wastewater.
OCD, Raman spectra, and 3DEEM fluorescence spectra. Parametric studies demonstrated that the ultimate [nitrosamines] increased at a pH range of 4.5–6.2, and with increasing [bromide], [ammonium], and current density. Conversely, sulfate and carbonate ions inhibited nitrosamine formation. Moreover, the implications of EC in urine-containing source waters were evaluated. The results indicate that regardless of the urine source (individual volunteers, septic tank, swimming pool, untreated municipal wastewater), high levels of nitrosamines (0.1–17.6 µg L−1) were generated, surpassing the potable reuse guideline of 10 ng L−1. Overall, this study provides insights to elucidate the mechanisms underlying nitrosamine formation and optimize the operating conditions. Such insights facilitate suppressing the generation of nitrosamine byproducts during electrochemical treatment of urine-containing wastewater.